What Is a Partial Knee Replacement?
A partial knee replacement is a type of knee surgery where only the damaged part of your knee joint is replaced, rather than the whole joint. It is often considered when arthritis is confined to just one section of the knee, allowing the healthy areas to be preserved.

Basic anatomy of the knee joint
Your knee is a complex hinge joint made up of three compartments:
- Lateral Compartment: Found on the outside of the knee, this connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia).
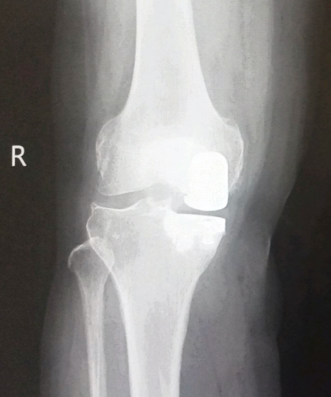
- Medial Compartment: Located on the inside of the knee, it also connects the femur and tibia. This area is often the first to show signs of wear from osteoarthritis, and is the most common area treated during a partial knee replacement surgery.
- Patellofemoral Compartment: The front of the knee, where the thigh bone meets the kneecap (patella).
Each compartment is lined with cartilage, which cushions the bones and allows smooth movement. When cartilage wears away, the bones can rub against each other, leading to pain and stiffness. This localised damage in 1 or 2 compartments of the knee allows treatment with partial knee replacement instead of total knee replacement.
How Partial Knee Replacement in Singapore Compares to Total Knee Replacement
Knowing whether a partial knee replacement or a total knee replacement is suitable for your condition can help you prepare for surgery and set realistic expectations for your recovery. Here’s how they differ:
1. Extent of Surgery
The extent of the knee joint that is replaced during surgery.
Partial Knee Replacement: Replaces or resurfaces only the damaged compartment of the knee, keeping the rest of the joint intact.
Total Knee Replacement: Replaces all compartments of the knee joint.
2. Recovery Time
How quickly you can expect to regain mobility after surgery.
Partial Knee Replacement: Often allows quicker recovery as more natural bone, ligaments, and muscle are preserved.
Total Knee Replacement: Recovery may take longer due to the larger surgical area and full joint replacement.
3. Implant Types
The design of the artificial components used to replace the knee.
Partial Knee Replacement: Uses implants designed for one compartment of the knee.
Total Knee Replacement: Uses implants shaped to replace the entire knee joint.
4. Patient Suitability
Who may benefit most from each type of knee replacement.
Partial Knee Replacement: Generally suited for patients with arthritis limited to single or two compartments.
Total Knee Replacement: Recommended when arthritis or damage affects most or all compartments of the knee.
Basic anatomy of the knee joint
Benefits of partial knee replacement
- Faster recovery time: Partial knee replacement typically involves a smaller incision, less bone removal, and less disruption of surrounding soft tissues than total knee replacement. This can result in a faster recovery time and less pain after surgery.
- Less blood loss: Partial knee replacement is associated with less blood loss than total knee replacement, which can be particularly beneficial for people with certain medical conditions or those who are at high risk for complications.
- More natural knee movement: Because only one part of the knee joint is replaced in a partial knee replacement, the joint may feel and move more naturally than in a total knee replacement. This can result in better range of motion and patient’s satisfaction score.
- Lower risk of complications: Because partial knee replacement is a less invasive procedure, it is associated with a lower risk of complications such as infection, blood clots, knee stiffness.
- Better preservation of healthy tissue: In a partial knee replacement, only the damaged part of the knee joint is replaced, which means that healthy tissue is preserved. This can be beneficial for people who may need additional knee surgery in the future.
It is important to note that not everyone is a good candidate for partial knee replacement. Your surgeon will consider factors such as the extent of your knee arthritis, your overall health, and your activity level when recommending the best treatment option for you.
1
Less invasive
A partial knee replacement typically involves a smaller incision, less bone removal, and minimal disturbance to surrounding soft tissues. These factors can contribute to quicker mobility and reduced post‑operative discomfort.
2
Less Blood Loss
There’s typically less blood loss with a partial knee replacement, which can be particularly beneficial for people with certain medical conditions or those who are at high risk for complications.
3
More Natural Knee Movement
With a partial knee replacement, only the affected part of the knee is replaced, preserving much of the joint’s natural structure. This can help maintain movement that feels more like your natural knee and support a good range of motion. Hence, better patient satisfaction score.
4
Lower Risk of Complications
Partial knee replacement surgery is generally less invasive, which may lower the chances of issues such as infection, blood clots, or stiffness — though these risks still exist.
5
Better Preservation of Healthy Tissue
Only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced, leaving healthy cartilage, ligaments, and bone untouched. Keeping these structures intact may be beneficial if future knee surgery becomes necessary.
Important: Not everyone is suited for a partial knee replacement in Singapore. Your orthopaedic surgeon will consider the extent of arthritis, your general health, and your activity level before recommending the best treatment option.
When to Consider Partial Knee Replacement in Singapore
Doctors often recommend partial knee replacement when damage is confined to just one part of the knee joint and when non‑surgical treatments no longer provide enough relief.
Here are some common signs that a partial knee replacement could be considered:
- Early‑Stage Osteoarthritis in One Compartment
When cartilage wear is limited to the inner (medial) or outer (lateral) compartment of the knee, the rest of the joint is still healthy and can benefit from a partial knee replacement. - Persistent Pain on One Side of the Knee
If you’ve tried medication, physiotherapy, or adjusting your activities but still have pain on just one side of your knee, it could mean the damage is limited to one area — something a partial knee replacement may help address. - Stable Ligaments and Good Joint Function
If your knee still feels stable and moves well because the ligaments and healthy compartments are intact, you may benefit from a partial knee replacement instead of a total knee replacement.

Recovery Tips After Partial Knee Replacement
Recovering well after a partial knee replacement will depend on following your surgeon’s advice, staying active while being safe, and supporting your body through good nutrition and self‑care. Here are some tips to help you:
- Follow Your Physiotherapy Plan
- Attend all physiotherapy sessions as scheduled.
- Do the recommended home exercises daily to strengthen your knee and improve flexibility.
- Increase your activity level gradually, avoiding movements that cause sharp pain.
- Keep Moving, Safely
- Walk short distances several times a day to improve circulation and prevent stiffness.
- Use walking aids like crutches or a cane if recommended, and transition to walking unaided when your doctor says it’s safe.
- Avoid high‑impact activities like running or jumping until cleared by your surgeon.
- Support Healing Through Nutrition
- Eat lean protein such as fish, chicken, tofu, and eggs to help repair tissue.
- Include colourful vegetables, whole grains, and calcium‑rich foods to support bone and joint health.
- Stay hydrated throughout the day.
- Manage Pain and Swelling
- Take pain medication only as prescribed by your doctor.
- Apply ice packs for short periods to reduce swelling.
- Elevate your leg when resting to promote circulation and reduce discomfort.
- Monitor Your Progress
- Keep track of improvements in movement, strength, and pain levels.
- Report any unusual symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, redness, or fever to your healthcare team immediately.
Recovering from a partial knee replacement is a gradual process. By following your rehabilitation plan and taking care of your overall health, you can steadily regain mobility and return to the activities you enjoy.
Common Myths About Partial Knee Replacement in Singapore Debunked
You may have some myths about partial knee replacement in Singapore that make you second‑guess the surgery. Let’s set the record straight.
Myth: Partial knee replacements don’t last long.
The Truth: Modern implants are designed to be durable and, with appropriate care, they can often function well for many years.
Myth: You have to be elderly to be suitable for partial knee replacement.
The Truth: Age is not the sole deciding factor. Your doctor will consider the condition of your knee, the location of damage, and your overall health to assess whether a partial knee replacement is the best option for you.
Myth: You can’t be active after partial knee replacement surgery.
The Truth: Many people are able to return to low‑impact activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, within weeks to months after surgery, once they have recovered well enough and their knee surgeon has given the go‑ahead.
Myth: Recovery for partial knee replacement is just as difficult as a total knee replacement.
The Truth: Because only one compartment of the knee is replaced, recovery is usually faster and less demanding than with a total knee replacement — though physiotherapy is still essential.
Myth: Partial knee replacement is always the best option.
The Truth: It’s not suitable for everyone. The procedure works best when arthritis or damage is limited to one compartment and your ligaments are healthy. If the damage is more widespread, a total knee replacement may be the better choice.
Choosing the Right Surgeon for Your Partial Knee Replacement in Singapore
Choosing the right knee surgeon in Singapore for your partial knee replacement can help set the tone for your care. Here are some important factors to consider.
- Qualifications and Accreditation
Make sure your knee surgeon in Singapore has:- A recognised basic medical degree (like a Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery, or equivalent) and is registered with the Singapore Medical Council.
- Completed a structured orthopaedic surgery residency accredited locally, ensuring they’ve had training in partial knee replacement in Singapore.
- A specialist certification, such as the Master of Medicine (Orthopaedic Surgery) or equivalent, and accreditation by the Specialists Accreditation Board.
- Professional Experience
Consider their:- Years in practice and experience with cases similar to yours.
- Proficiency in both total and partial knee replacement procedures.
- Involvement in teaching, research, or leadership roles.
- Patient Feedback and Reputation
While no patient experience is identical, feedback can offer insights into a surgeon’s communication style, professionalism, and approach to care.
You can:- Ask for recommendations from trusted healthcare professionals, friends, or family.
- Read patient reviews on the clinic’s website, Google, or other platforms — keeping in mind that individual experiences may vary.
- Check the reputation of the surgical facility for aftercare support.
- Surgical Approach and Communication
Look for a partial knee replacement surgeon in Singapore who:- Explains the range of treatment options with you.
- Clearly outlines the procedure.
- Discusses the benefits and potential risks of each procedure.
- Practical Considerations
When choosing a partial knee replacement surgeon in Singapore, you should also think about:- The clinic’s location, accessibility, and follow‑up arrangements.
- Whether your procedure is covered by your insurance or Medisave scheme.
- Whether the surgeon communicates well in your preferred language.
Frequently Asked Questions
Arthritis or injury affecting only one or 2 knee compartment, often seen in early‑stage osteoarthritis.
A partial knee replacement only replaces one damaged compartment. A total one replaces all compartments of the knee joint.
Risks include infection, blood clots, stiffness, fracture, implant loosening, or arthritis developing elsewhere.
How do surgeons in Singapore determine if partial knee replacement is the right choice for patients?
Through physical exams, X‑rays, and sometimes MRI, to assess joint damage and ligament health.
Light activity may be resumed in weeks. Full recovery often takes several months with physiotherapy.
Through strict safety protocols and structured post‑surgery rehabilitation.


